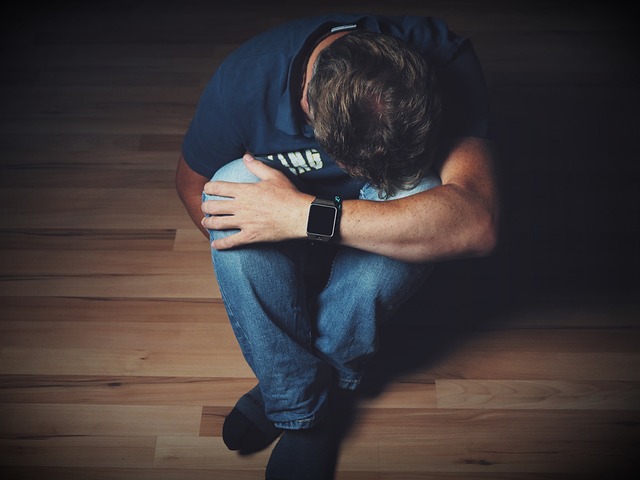

Addiction is a multifaceted brain disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to use substances like alcohol or drugs, even when faced with negative outcomes. Those suffering from addiction are often consumed by the need to consume these substances, allowing it to dominate their daily existence. Despite being aware of the potential issues it may cause, they continue their usage.
The effects of addiction extend far beyond immediate physical symptoms. In the long term, addiction can damage almost every part of the body, leading to chronic health conditions, mental health disorders, and even a reduced life expectancy. The impact of addiction on health over a lifetime can be profound and far-reaching, affecting not just the individual, but also their family, friends, and the broader community.
Understanding the long-term health implications of addiction is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This offers a clearer view of the challenges faced by those struggling with addiction and the importance of sustained support and care.
Contents
Addiction manifests in various forms, primarily categorized into substance and behavioral addictions. Substance addiction involves the compulsive use of substances like alcohol, nicotine, or drugs, whereas behavioral addiction includes compulsive behaviors such as gambling or overeating. These addictions, though different in their objects of fixation, share a common thread: the overwhelming urge to repeat behaviors despite negative consequences.
On a psychological level, addiction often stems from a need to escape reality, cope with stress, or fill an emotional void. Physiologically, addictive substances and behaviors can alter brain chemistry, leading to dependence. This dependence creates a cycle where individuals crave the substance or behavior to feel normal.
Statistics paint a concerning picture of addiction’s prevalence. Globally, millions are affected, with substance abuse disorders alone impacting a significant portion of the population. The numbers reveal a widespread struggle, highlighting the importance of understanding addiction’s nature to combat its far-reaching effects.
Addiction takes a heavy toll on an individual’s physical health. Regular abuse of substances can lead to severe liver damage, a critical organ for metabolizing and detoxifying substances entering the body. Heart disease is another common consequence, as addiction often drives behaviors that strain the heart, like increased blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms. These physical impacts are not just limited to internal organs; they often manifest in diminished health, making the body more susceptible to illnesses.
Mental health is equally impacted by addiction. Prolonged substance abuse often leads to or worsens mental health disorders like depression and anxiety. This, in turn, creates a vicious cycle where individuals use substances to cope with their emotional pain, only to find that their mental health deteriorates further, as seen by experts from addiction treatment San Diego. This decline in mental health can lead to a sense of isolation, loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, and an overall decrease in life satisfaction.
The social consequences of addiction are profound and far-reaching. Relationships suffer as the person battling addiction might become withdrawn or erratic, straining connections with family and friends. In the workplace, addiction can lead to decreased productivity, absenteeism, and even job loss. This deterioration of professional life further exacerbates the sense of isolation and can lead to financial instability.
Over time, addiction can lead to a series of chronic diseases. For instance, prolonged alcohol use is known to cause liver cirrhosis, a condition where healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. Similarly, long-term smoking increases the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer. These conditions don’t develop overnight but are the result of years of substance abuse, gradually wearing down the body’s defenses and resilience.
Furthermore, prolonged substance abuse can lead to changes in the brain’s structure and function, affecting areas responsible for decision-making, judgment, learning, memory, and behavior control. These changes can persist long after the substance use has stopped, indicating the deep and enduring impact of addiction on the brain. This alteration in brain function can make recovery challenging, as the brain needs time and support to heal and regain its normal functioning.
Recognizing these long-term effects is crucial in understanding the full scope of addiction’s impact on an individual’s health. It underscores the importance of early intervention and sustained support for those struggling with addiction.
The road to recovery from addiction is multifaceted, involving various treatment options. Medical treatments, such as detoxification and medication-assisted therapies, are often the first steps. These methods help in safely managing withdrawal symptoms and reducing cravings. Following medical treatment, counseling and behavioral therapies play a crucial role. They address the root causes of addiction, helping individuals understand and change their behaviors and coping strategies.
In addition to formal treatments, lifestyle changes are pivotal in recovery. Adopting a healthy diet improves physical health, which is often compromised due to addiction. Regular exercise boosts mood and energy levels, aiding in combating depression and anxiety commonly associated with recovery.
Establishing a stable routine and engaging in positive social activities also contribute significantly to maintaining sobriety. These lifestyle changes support the physical aspect of recovery and reinforce mental well-being, providing a solid foundation for an addiction-free life.
Early education on addiction is crucial. It equips individuals with knowledge about the consequences of addiction, both short-term and long-term. This understanding helps in making informed decisions regarding substance use. Furthermore, education fosters empathy and compassion toward those struggling with addiction, thereby reducing stigma and promoting a supportive environment.
The role of community and family support in preventing addiction cannot be overstated. A supportive family environment offers a safety net for individuals facing challenges. It provides emotional support, which is essential in resisting the lure of addictive behaviors. Community support, including access to resources and peer support groups, creates a network of care. This network can intervene early, offer help, and prevent the escalation of substance use into addiction.
Conclusion
Addiction profoundly affects an individual’s health throughout their life. From immediate physical and mental health impacts to long-term chronic conditions, its effects are far-reaching. Recovery is possible, though it requires comprehensive treatment and lifestyle changes.
Understanding addiction’s extensive impact is crucial. It helps in developing effective strategies for treatment, recovery, and prevention. This awareness can lead to more supportive environments. It can foster healthier lifestyles, benefiting individuals and society as a whole.
The year 2020 and the pandemic threw a wrench into everyone's plans. Companies that were…
AI is successful in boosting the productivity of organizations while helping them save cost and…
Suppose you battle back discomfort or other associated ailments due to sitting for lengthy periods…
In November 2023, investor Maksym Krippa acquired the Parus Business Center, redefining the commercial real…
Programmers create computer programs, mobile solutions and also analyse the needs of their clients and…
A trip to Santiago is sure to be memorable by default as simply seeing this…